Understanding Healing Trauma
Healing trauma is an intricate process that requires a deep understanding of what trauma is and how it affects our lives. Trauma can shape our mental health, influence our relationships, and alter our perception of safety and enjoyment in the world. By embarking on a journey toward healing trauma, individuals can reclaim their sense of self, establish healthy relationships, and lead fulfilling lives. This article aims to explore the various facets of healing trauma, including its definition, impact, signs indicating the need for healing, effective approaches, and resources available for support. For those seeking information or pathways to healing trauma, healing trauma encompasses a wide range of topics that can provide essential guidance.
What is Trauma?
Trauma refers to the emotional and psychological response to an extreme event or series of events that can cause lasting adverse effects on an individual. It may arise from experiences such as physical or emotional abuse, natural disasters, loss of a loved one, accidents, or other overwhelming circumstances. The complexity of trauma lies in its subjective interpretation; what one person finds traumatic, another may perceive differently. The classification of trauma can be broadly categorized into two types: acute trauma, stemming from a single incident, and chronic trauma, which is the result of enduring and repetitive distressing events.
The Impact of Trauma on Mental Health
The impact of trauma on mental health can be profound and far-reaching. Individuals may experience a range of symptoms, including anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and complex PTSD. These symptoms can manifest in various forms, disrupting daily life and leading to difficulties in social interactions, work performance, and personal relationships. Neurobiologically, trauma can result in changes in brain structure and function, particularly in the areas governing stress response, emotions, and memory. Additionally, trauma can influence a person’s ability to cope with stress and create a heightened sense of vulnerability.
Different Types of Trauma
Understanding the different types of trauma is critical to addressing its effects. The primary types include:
- Acute Trauma: short-term psychological response to a single traumatic event.
- Chronic Trauma: long-term psychological effects resulting from repeated traumatic exposure.
- Complex Trauma: exposure to multiple traumatic events, often of an interpersonal nature, typically occurring in childhood.
- Secondary Trauma: experiences of individuals who witness or are indirectly affected by trauma, often seen in caregivers or professionals working in trauma-related fields.
Signs Indicating You Need Healing Trauma
Recognizing the signs of trauma is essential for initiating healing. While the effects of trauma may vary significantly from person to person, there are common indicators across various stages of recovery.
Physical Symptoms of Trauma
Physical symptoms can often be overlooked but are crucial in identifying trauma. These may include:
- Chronic pain or unexplained physical ailments
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Changes in appetite or weight fluctuations
- Increased startle response or hyper-vigilance
Emotional and Behavioral Indicators
Emotional and behavioral changes can significantly signal the need for healing trauma. Common indicators include:
- Increased irritability, aggression, or mood swings
- Withdrawal from social activities or isolation
- Difficulty concentrating or making decisions
- Experiencing intense fear or anxiety when faced with reminders of the trauma
Long-Term Effects on Wellbeing
Long-term effects of trauma on overall wellbeing can lead to severe repercussions, as unresolved trauma may establish enduring patterns of behavior. These effects can manifest in:
- Substance abuse or other self-destructive behaviors
- Chronic health problems not attributable to other causes
- Difficulty forming or maintaining relationships
- Pervasive feelings of hopelessness or despair
Approaches to Healing Trauma
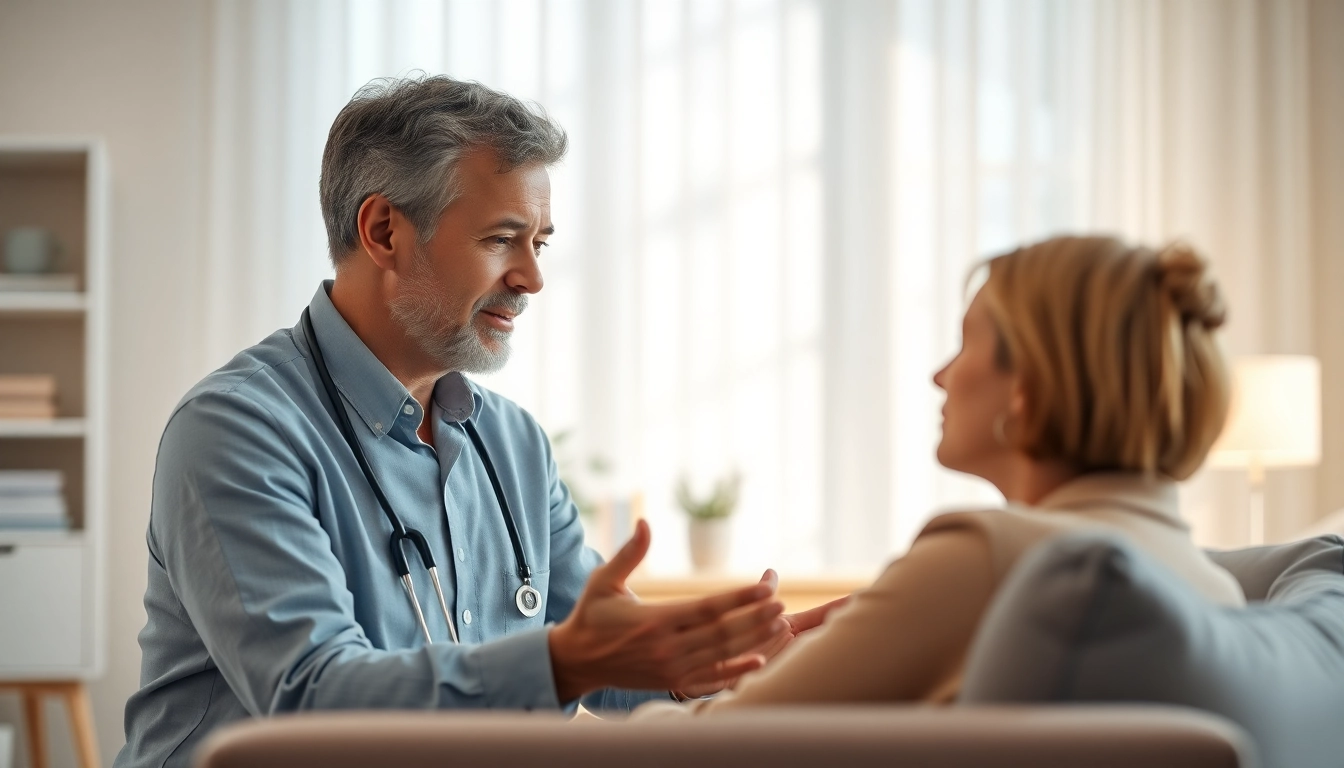
When it comes to healing trauma, multiple strategies and therapeutic approaches can be tailored to the individual’s needs. Finding the right method is critical as everyone experiences trauma differently.
Therapeutic Options for Healing Trauma
Engaging with professional therapy is often beneficial. Various therapeutic modalities are effective in healing trauma, including:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): addresses negative thought patterns and behaviors to foster healthier mental processing.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): designed specifically for trauma recovery, helping integrate traumatic memories.
- Somatic Experiencing: focuses on the physical sensations related to trauma stored in the body.
- Art and Music Therapy: allows individuals to express trauma non-verbally through creative means.
Self-Help Techniques
In addition to professional therapy, self-help techniques can significantly contribute to healing trauma. Practical methods include:
- Regular physical exercise, which can reduce stress hormones and enhance mood.
- Journaling to articulate feelings and confront traumatic memories.
- Practicing grounding techniques to remain present during overwhelming moments.
- Engaging in relaxation practices such as yoga and mindfulness meditation.
Community and Support Networks
Finding support from community and family can also play a crucial role in the healing process. Support groups, both in-person and online, can offer empathy and understanding from those who have shared similar experiences. Building a support network allows individuals to connect with others, share coping strategies, and foster a sense of belonging.
Integrating Healing Trauma into Daily Life
Once individuals begin their healing journey, it is important to integrate new practices and supportive habits into daily life to foster long-term recovery and resilience.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Effective coping mechanisms are essential for managing symptoms and creating a resilient mindset. These can include:
- Structuring daily routines that provide a sense of control and stability.
- Establishing healthy boundaries in relationships to avoid overwhelming triggers.
- Practicing self-compassion and understanding that healing takes time.
Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
Mindfulness and meditation practices can help ground individuals in the present, reduce anxiety, and promote overall mental health. Techniques may include:
- Mindful breathing to center focus and reduce tension.
- Body scans to enhance awareness of physical sensations and foster relaxation.
- Guided imagery to visualize peaceful and safe places, aiding in emotional regulation.
Building Resilience for the Future
Building resilience is an ongoing process crucial for recovery and facing life’s challenges with confidence. Strategies include:
- Engaging in regular self-reflection to foster personal growth and self-awareness.
- Setting realistic goals and celebrating small achievements along the path to recovery.
- Developing a gratitude practice to shift focus from negative experiences to positive aspects of life.
Resources and Next Steps for Healing Trauma
Identifying resources and support systems is vital for initiating the healing process. Many tools and services are available to aid individuals on this journey.
Recommended Reading and Materials
There are numerous books and materials available that educate and provide support for those healing trauma. Key recommendations include:
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel van der Kolk – a deep exploration of how trauma affects the body.
- Healing Trauma: A Pioneering Program for Restoring the Wisdom of Your Body by Peter A. Levine – a guide on understanding and overcoming trauma.
Workshops and Online Courses
Participating in workshops and online courses can offer structured education and tools for trauma recovery. Many organizations provide resources ranging from mindfulness training to advanced therapeutic techniques.
Professional Help: Finding the Right Therapist
Finally, seeking professional help can be a critical step towards healing. When choosing a therapist, consider their specialization in trauma-informed care and their approach to healing. Personal chemistry and comfort are essential components of a successful therapeutic relationship, therefore, it is important to take the time to find the right fit.














Leave a Reply