Understanding Hydrogen Detectors
Hydrogen, a colorless, odorless, and highly flammable gas, poses significant safety risks, especially in industrial and laboratory settings. Efficient monitoring of hydrogen levels is essential for maintaining safe environments, which is where a hydrogen detector comes into play. This article delves into the fundamentals of hydrogen detectors, exploring their workings, applications, types, and maintenance requirements, as well as industry compliance standards.
What is a Hydrogen Detector?
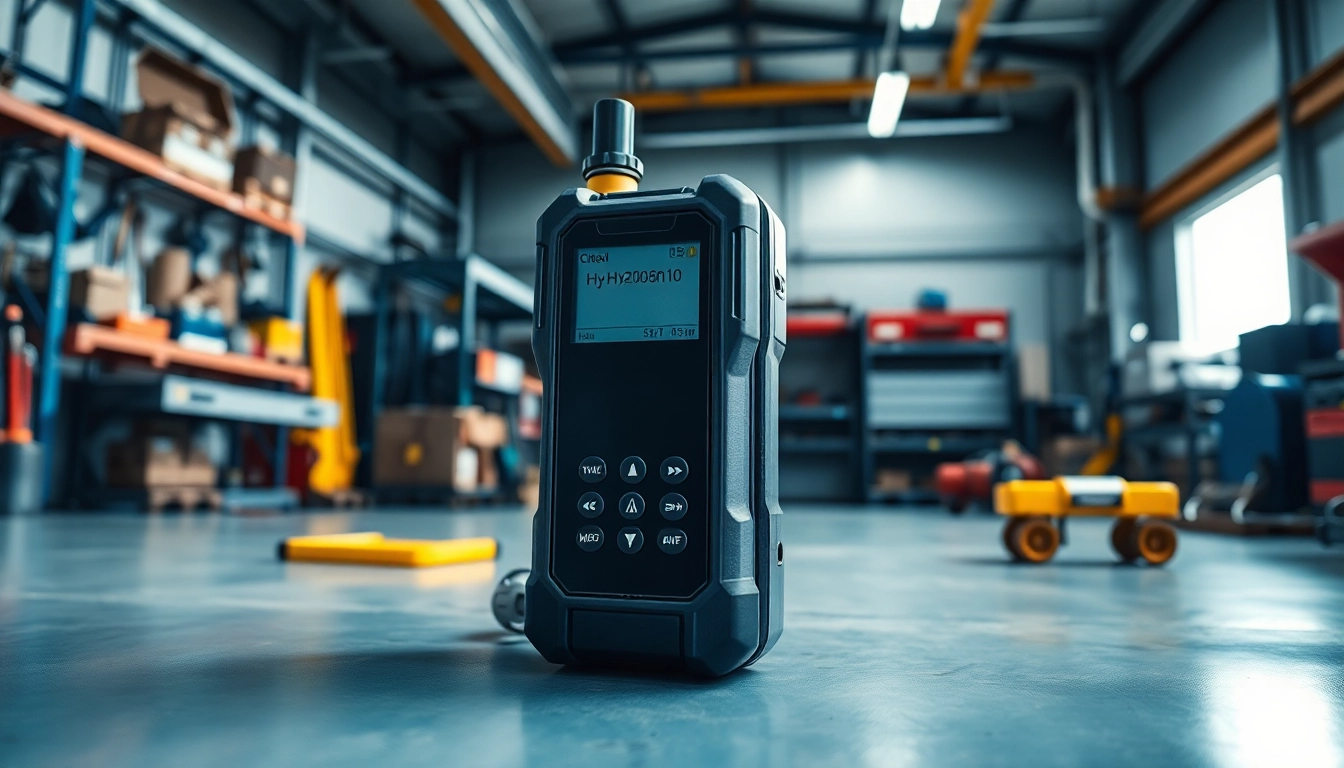
A hydrogen detector is a specialized device designed to detect the presence of hydrogen gas in various environments. It ensures that safety protocols are adhered to and that any dangerous gas accumulation is identified swiftly. These detectors serve as crucial components in settings such as laboratories, battery rooms, and industrial operations where hydrogen is utilized.
How Does a Hydrogen Detector Work?
The operation of hydrogen detectors typically relies on advanced sensor technology. Most devices use metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensors, which alter their electrical conductivity when exposed to hydrogen. When hydrogen gas comes into contact with the semiconductor material, it reduces the oxidation state of the metal oxide, leading to a measurable change in conductivity. This change is directly correlated to the concentration of hydrogen in the environment, allowing for precise measurements that trigger alarms or shutdown systems if dangerous levels are reached.
Common Applications of Hydrogen Detectors
Hydrogen detectors have a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Battery Manufacturing: Monitoring hydrogen levels in battery rooms to prevent explosive environments.
- Petrochemical Industries: Ensuring safety in facilities that handle hydrogen during refining processes.
- Research Laboratories: Monitoring experimental setups that involve hydrogen to safeguard researchers.
- Automotive Industry: Used in hydrogen fuel cell technology for vehicle production and testing.
- Hydrogen Production Facilities: Verifying gas levels during hydrogen generation processes.
Types of Hydrogen Detectors
Portable Hydrogen Detectors
Portable hydrogen detectors are compact, handheld devices ideal for personal safety in environments where hydrogen might be present. They provide real-time monitoring and are particularly useful for personnel moving between different areas of a facility. The portability aspect allows for easy use and immediate alerts to individuals working close to potential hydrogen leaks. Many modern portable detectors come equipped with features such as built-in data logging, alarms, and even Bluetooth connectivity for enhanced safety management.
Fixed Hydrogen Detectors
Fixed hydrogen detectors are permanently installed units that continuously monitor hydrogen concentrations within a specific area. They are essential for maintaining safety in locations with a high risk of gas accumulation, such as battery storage facilities. These detectors can be integrated into a facility’s overall safety systems, linking with ventilation controls and alarm systems to enhance response readiness in emergencies.
Multi-Gas Detectors Versus Single-Gas Detectors
When selecting a hydrogen detection system, users often face the decision between multi-gas and single-gas detectors. Single-gas detectors are dedicated to hydrogen monitoring and are typically more straightforward and less expensive. In contrast, multi-gas detectors can monitor various gases simultaneously, making them versatile tools for environments with multiple hazardous substances. The choice between the two generally depends on the specific needs of the facility and the potential presence of other gases.
Choosing the Right Hydrogen Detector
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Detector
Choosing the right hydrogen detector requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Detection Range: Ensure the detector can effectively measure the required concentration of hydrogen.
- Type of Sensor: Consider sensor technologies available, such as catalytic, electrochemical, or MOS sensors, and their applicability to your environment.
- Response Time: The ability of a detector to quickly respond to rising gas levels is crucial for preventing incidents.
- Durability: Look for models designed to withstand harsh industrial environments.
- Calibration Needs: Understand the calibration requirements and how they affect the overall maintenance of the detector.
Top Brands and Models on the Market
Numerous brands manufacture hydrogen detectors, each offering various models tailored for different applications. Some of the most reputable brands include:
- Honeywell: Known for robust portable and fixed solutions, widely used in industrial settings.
- Industrial Scientific: Offers a range of multi-gas detectors that include hydrogen as part of their detection capability.
- FORSCOM: Renowned for high-precision hydrogen detectors suitable for fieldwork and inspections.
- GasLab: Provides fixed gas detectors that meet stringent safety requirements.
Price Comparison and Budgeting
The price of hydrogen detectors varies significantly based on their type (portable versus fixed), brand, and features. On average, portable detectors may range from $300 to $1,500, whereas fixed installations can cost from $1,000 to several thousand dollars depending on complexity. It’s essential to factor in both initial costs and ongoing maintenance and calibration expenses when budgeting for hydrogen detection systems.
Installation and Maintenance
Steps for Installing a Hydrogen Detector
Proper installation of hydrogen detectors is critical to ensure accurate functioning. Here are key steps for installation:
- Site Assessment: Evaluate the area where the detector will be installed, identifying potential hydrogen sources and airflow patterns.
- Determine Placement: Position the detector at an optimal height based on the expected accumulation zones. Hydrogen is lighter than air, so installation near the top of the room is preferred.
- Electrical Requirements: Ensure that the site meets electrical requirements and that power sources are accessible if the detector is not battery-operated.
- Calibration: Calibrate the detector according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure accuracy upon installation.
- Testing: After installation, conduct tests to confirm that the detector is functioning properly and can respond to hydrogen presence effectively.
Best Practices for Maintenance
Regular maintenance of hydrogen detectors is essential for ensuring long-term functionality and reliability. Some best practices include:
- Routine Calibration: Follow the manufacturer’s guidance on the frequency of calibration, typically at least once a year.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect the detectors for any signs of damage, wear, or dirt that may interfere with performance.
- Battery Checks: For portable detectors, regularly check and replace batteries to prevent failures during operation.
- Training Personnel: Ensure that staff are trained on how to operate detectors and recognize alarm signals properly.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the most reliable hydrogen detectors can experience issues over time. Common problems include:
- False Alarms: These can occur due to environmental factors like humidity. Regular calibration and sensor cleaning can mitigate this issue.
- Slow Response Time: This may indicate a need to recalibrate or replace the sensors.
- Inconsistent Readings: Check the detector for obstructions or contaminants on the sensor surface.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
Understanding Industry Standards for Hydrogen Monitoring
Hydrogen detectors must comply with several industry safety standards to ensure they operate effectively and reliably. Standards such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) guidelines typically govern hydrogen safety protocols in workplaces. The Underwriters Laboratories (UL) certification ensures that detectors meet safety and performance benchmarks.
Compliance with Safety Regulations
Compliance with various regulations concerning gas detection is non-negotiable for many businesses. Organizations such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) provide frameworks that companies must adhere to when it comes to workplace safety. Regular audits and adherence to regulations help prevent accidents related to hydrogen gas.
Case Studies on Hydrogen Detection Systems in Use
Examining real-world implementations of hydrogen detection systems provides insights into their effectiveness and value:
- Battery Manufacturing: A major battery manufacturer integrated a fixed hydrogen detection system in their production facility to monitor gas levels constantly. As a result, the company reduced the number of safety incidents linked to hydrogen accumulation significantly.
- Research Laboratories: A laboratory conducting hydrogen fuel cell experiments adopted portable hydrogen detectors. This move allowed researchers to confidently work with flammable materials, ensuring they were alerted to any gas leaks promptly.
- Petrochemical Industry: A petrochemical plant installed multiple hydrogen detectors throughout their facility to comply with stringent industry regulations, leading to improved safety ratings and reduced risk of incidents.













Leave a Reply