Understanding Laminating Resin
What is Laminating Resin?
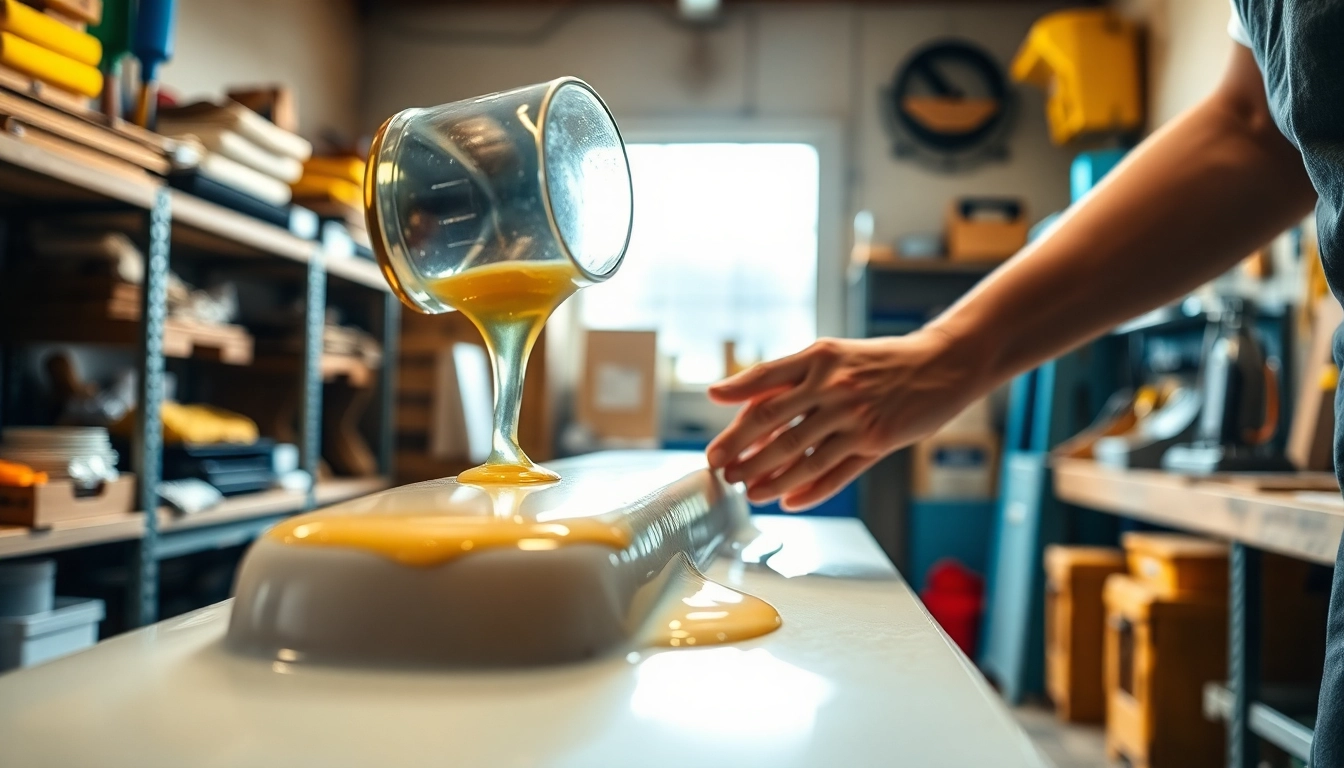
Laminating resin is a crucial material widely utilized in various composite applications, primarily for bonding layers of materials together. It is specifically designed for use with fibrous materials, such as fiberglass, to create strong and durable composites. The primary function of this resin is to effectively saturate the fibers, forming a robust bond that enhances structural integrity.
Laminating resin is typically formulated to exhibit excellent adhesion, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making it suitable for demanding environments. It often comprises two main categories: polyester and epoxy resins. Polyester resins are known for their affordability and straightforward application, while epoxy resins provide superior strength and thermal resistance. Understanding the foundational aspects of laminating resin is pivotal for anyone looking to engage in projects involving composites, whether in marine, automotive, or construction applications.
Common Types of Laminating Resin
The classification of laminating resin can greatly impact the end-use properties of the material being produced. Below are the primary categories:
- Polyester Laminating Resin: Known for its cost-effectiveness, polyester laminating resins are commonly used in marine applications, repairs, and general-purpose bonding. They cure quickly, providing adequate working time for laying up fiberglass.
- Epoxy Laminating Resin: This type offers superior strength and adhesion, making it ideal for high-performance applications where durability is crucial. Epoxy can withstand higher temperatures and environmental stressors compared to polyester.
- Vinyl Ester Laminating Resin: Vinyl ester resin provides enhanced resistance to water and chemicals, making it a preferred choice in aggressive environments. It also exhibits lower shrinkage characteristics than polyester.
Applications of Laminating Resin
Laminating resin finds applications across diverse industries due to its versatile properties. Some notable applications include:
- Marine Industry: Used to build boats and components due to its waterproof qualities and ability to bond fiberglass layers securely.
- Aerospace Sector: Essential in the reinforcement of fuselage structures and other components where weight and durability are critical.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Employed in creating stronger, lighter parts and body components, laminating resin helps improve fuel efficiency and performance.
- Construction: Used for creating composite materials that require strength and resilience in architectural structures and products.
Choosing the Right Laminating Resin for Your Project
Factors to Consider When Selecting Laminating Resin
Selecting the appropriate laminating resin involves several critical factors:
- Performance Requirements: Understanding the mechanical properties required for the application will guide resin selection.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to chemicals, moisture, heat, and UV light should influence the choice between polyester, epoxy, and vinyl ester resins.
- Working Time: How quickly the resin cures is essential for the application process, especially in production environments.
- Cost Considerations: Budget constraints may dictate the choice of resin; while epoxy is more expensive, its properties might justify the cost.
Evaluating Resin Properties
To ensure the selected laminating resin meets application demands, it’s critical to evaluate these properties:
- Viscosity: Affects how easily the resin can be applied and whether it penetrates and saturates fiberglass properly.
- Tensile Strength: This measures the resin’s resistance to being pulled apart, crucial for structural applications.
- Elongation at Break: Indicates how much strain the resin can withstand before breaking, important in applications subject to vibrations and impacts.
- Cure Time: Time taken for the resin to reach optimal strength, which can influence project timelines.
Matching Resin to Application Requirements
Each application may require specific resin characteristics. For example, a marine project would benefit from a polyester laminating resin with excellent waterproof properties, while aerospace projects might necessitate a high-performance epoxy resin for structural applications. Matching the resin’s characteristics with the application’s needs ensures optimal performance and longevity, helping to avoid potential failures or safety issues.
Techniques for Working with Laminating Resin
Preparing the Surface for Laminating Resin
The success of laminating resin applications largely depends on surface preparation. Proper preparation involves cleaning, sanding, and priming the surfaces that will be bonded.
- Cleaning: Remove dust, grease, and oils using solvents or detergents to enhance adhesion.
- Sanding: Roughen the surface with sandpaper; this improves bonding by providing texture for the resin to cling to.
- Priming: In some cases, a primer can enhance adhesion, especially when working with shiny surfaces.
Best Practices for Application
Applying laminating resin requires specific techniques to ensure the best results:
- Measured Mixing: Follow manufacturer recommendations for mixing resin and hardener for optimal performance.
- Layering Techniques: Apply the resin in thin, even layers to ensure complete saturation of fiberglass.
- Temperature Control: Work within the optimal temperature range specified by the manufacturer, as this affects curing and performance.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding potential pitfalls can significantly impact the success of projects involving laminating resin:
- Incorrect Mixing Ratios: Failing to adhere to mixing guidelines can result in incomplete curing or weakened bonds.
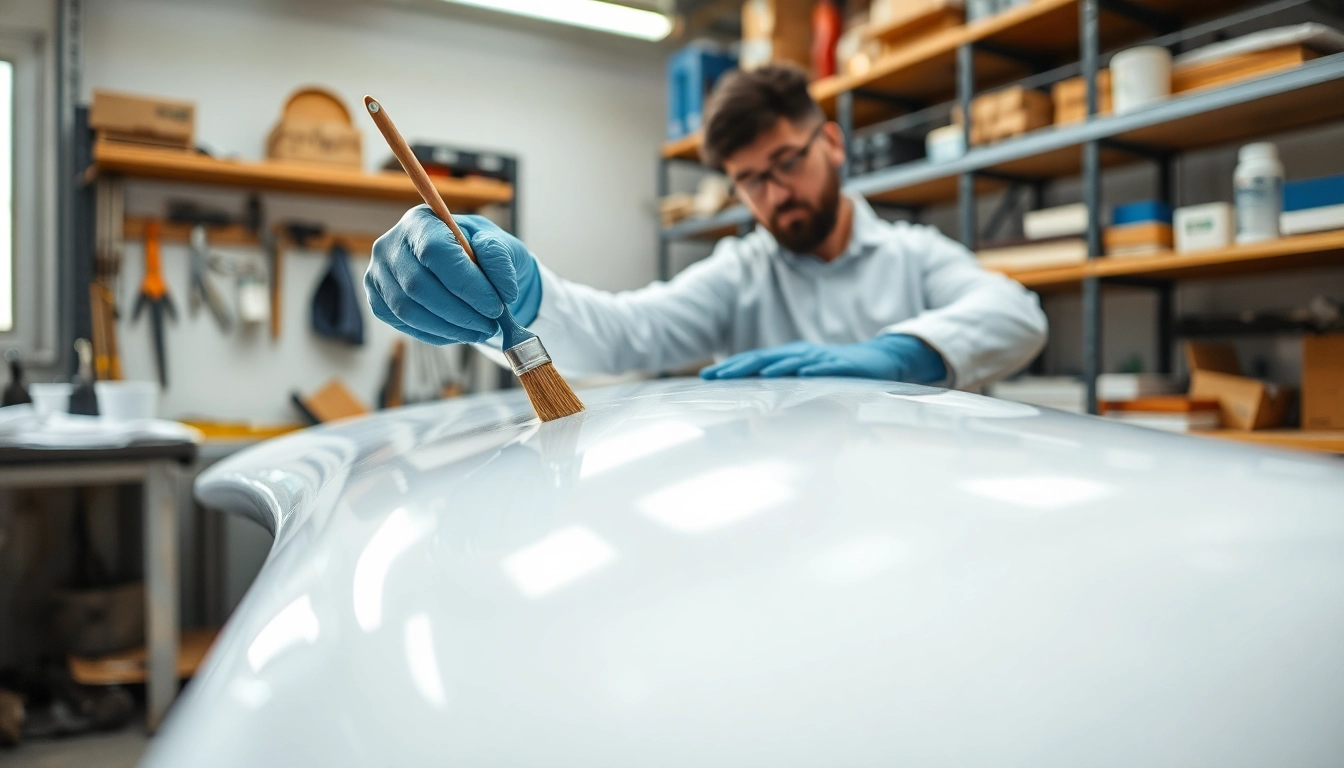
- Neglecting Safety Precautions: Not using protective gear during application can lead to health hazards.
- Rushing the Cure: Extreme environmental conditions or haste can impede optimal curing and final product integrity.
Health and Safety Considerations
Protective Gear for Laminating Resin Usage
Safety should be a priority when working with laminating resin. Appropriate protective gear includes:
- Gloves: Chemical-resistant gloves prevent skin contact with harmful substances.
- Respirator Masks: Protect against harmful fumes, especially in poorly ventilated spaces.
- Goggles: Safety goggles protect the eyes from splashes and irritants.
Handling and Storage of Laminating Resin
Proper handling and storage can significantly prolong the life of laminating resin products:
- Storage Conditions: Keep resin in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight to prevent degradation.
- Container Type: Store in original containers or chemical-resistant buckets to avoid contamination.
- Labeling: Clearly label all containers to prevent misuse and ensure safety.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
Laminating resins can have environmental implications. Proper disposal and recycling should be prioritized. Many formulations can be hazardous; thus, follow local regulations regarding disposal. Unused resin should not be poured down drains or disposed of in regular trash. Instead, seek out specialized disposal services or recycling programs for composite materials. This not only protects the environment but also ensures compliance with environmental regulations.
Advanced Applications of Laminating Resin
Innovative Techniques in Laminating Resin Use
The use of laminating resin is evolving, with innovative techniques enhancing their functionality. One notable advancement is the integration of nano-particles into laminating resin formulations, which can significantly enhance properties such as strength, scratch resistance, and aging. Additionally, the use of hydrophobic additives allows for self-cleaning properties in construction applications, promoting longevity and reducing maintenance overhead.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Numerous industries showcase the benefits of laminating resin in real-world applications:
- Marine Construction: Boats built using epoxy laminating resin demonstrate superior durability and performance under varied maritime conditions.
- Automotive Parts Production: The automotive industry has harnessed laminating resin to create lightweight components that reduce overall vehicle weight while enhancing safety features.
- Aerospace Applications: Recent projects have utilized advanced laminating techniques with epoxy resins, resulting in lighter structures without compromising structural integrity, thus improving fuel efficiency.
Future Trends in Laminating Resin Technology
The future of laminating resin technology is promising, with trends suggesting a shift towards more sustainable formulations. Bio-based resins are gaining traction as industries seek greener alternatives without sacrificing performance. Moreover, advancements in 3D printing of composite materials are opening new avenues for laminating resin applications, allowing for rapid prototyping and custom fabrications.












Leave a Reply